Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is a broad term for skin discoloration or darkening in several areas on the face and body. Some of the most common causes for this skin condition include:
- prolonged UV exposure
- hormonal fluctuations occurring during pregnancy
- genetics
- medical conditions such as Addison’s disease and hemochromatosis


SUCCESS CASES
*Due to MOH guidelines in Singapore, medical clinics cannot show before & after photos on their websites. However, we would be delighted to showcase our photographs and actual results during your in-clinic consultation with us.
Our Doctors
VIEW ALL
Dr. SK Tan
Special Interest
- Hyper-pigmentation
- Anti-Aging
- Acne
- Acne Scarring
- Ingredient Studies
Dr. SK Tan
Dr Tan graduated in 1971, with a Bachelors of Medicine (MB) and a Bachelors of Surgery (BS) from the University of Malaya. Dr Tan’s interest in dermatology led him to train at the St John’s Institute of Dermatology in London in the 1970s and he has since been focused in the field of aesthetic dermatology.
- MBBS
- Diploma in Venereology (University of London)
- Diploma in Dermatology (University of Wales)
- Diploma in Cosmetic Science (UK)
- Master of Business Administration
- Fellow of the American Academy of Dermatology (FAAD)
He is a member of numerous medical associations, including the American Academy of Dermatology, the International Society of Cosmetic Laser Surgeons, and the International Academy of Cosmetic Dermatology. Dr Tan was one of the first local doctors to be certified by the American Board of Anti-Aging Medicine. His personal interest in pigmentary disorders and acne has also led him to become an International Member of the Pigmentary Disorders Society of India, the Asian Society of Pigment Cell Research, and the American Acne and Rosacea Society (AARS).
Dr Tan’s work has led him to be invited to speak at numerous international conferences in the US, Europe and throughout the Asia Pacific region. He is a co-editor of “Handbook of Cosmetic Microbiology”, a reference book published by Marcel Dekker, and his papers have been published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, International Journal of Dermatology, Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy, and Expert Review of Dermatology, and has contributed a chapter in the reference book ‘Pigmentary Disorders: A Comprehensive Compendium’.
Special Interest
- Hyper-pigmentation
- Anti-Aging
- Acne
- Acne Scarring
- Ingredient Studies

Dr. Ben Yim
Special Interest
- Anti-aging
- Hyper-pigmentation
- Body-Contouring
- Fat Reduction
Dr. Ben Yim
Dr Yim graduated from Monash University in Australia with a Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery degree. He has also earned a Master of Science in Clinical Dermatology from the University of London and more recently in Non-Surgical Facial Aesthetics from Anglia Ruskin University in UK, as well as a Graduate Diploma in Family Physicians in National University of Singapore.
- M.B.B.S (Monash University) 1994
- Diploma Practical Dermatology (University of Wales College of Medicine) 1998
- MSc. Clinical Dermatology (University of London) 1999
- MBA (University of Chicago) 2011
- MSc Non-Surgical Facial Aesthetics (Anglia Ruskin) 2018
- GDFM (NUS) 2019
Dr Yim has been practicing aesthetic medicine in private practice since 2000. The former director of Clinical Aesthetics & Laser Centre has been offering a wide armamentarium of aesthetic services including Botulinum Toxins, fillers for facial enhancement, skin tightening, fractional lasers, threadlifts, and non-invasive body contouring treatments.
As a trainer for Allergan Medical Institute in Singapore, Dr Yim has been invited to speak and train for numerous aesthetic workshops and conferences including “The Advanced Facial Anatomy and Injectables Workshop”, Botulinum Toxins and Filler injectable training workshops organized by Allergan, “The Singapore Disease Conference 2008” and “1st International Conference on Healthcare Transformation 2008” and Forum for Professional Self-regulation jointly organized by the SingHealth Centre for Health Services Research and the NUS Medical Society, to name a few.
Dr Yim comes from a family of four doctors, all in private practice in family medicine. Despite the move into full-time aesthetic medicine, Dr Yim has also taken an interest in family medicine pursuing a Master degree in Medicine in Family Medicine in NUS in which he hopes to complete in 2020.
Outside of his profession, Dr Yim also actively participates in social projects such as tattoo laser removal for prison inmates and teenage delinquents. For leisure, he enjoys golf, reading, playing the piano and running – he has participated in several half-marathons.
Special Interest
- Anti-aging
- Hyper-pigmentation
- Body-Contouring
- Fat Reduction

Dr. Liz Lum YX
Special Interest
- Acne
- Acne Scarring
- Fillers
- Neurotoxin Injection - Botulinum Toxins
- Face Lifting
- Facial Slimming and Contouring
Dr. Liz Lum YX
Dr Liz Lum YX graduated from Trinity College in Dublin with a Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery degree. She has also earned a graduate diploma in aesthetic medicine with the American Academy of Aesthetic Medicine (AAAM). Apart from these, Dr Lum has also attained certification by the Ministry of Health accredited bodies under the Singapore Medical Council’s Aesthetics Dermatology Education Group for various aesthetics procedures. Before joining IDS, Dr Liz Lum YX was a surgical trainee with the hand surgery department in SGH.
- MBBCH BAO (Trinity College Dublin)
- Diploma in Aesthetic Medicine, American Academy of Aesthetic Medicine
- Accredited by the Aesthetic Practice Oversight Committee (Singapore Medical Council) for Certificates of Competence in Aesthetic Procedures
- Diploma in Cosmetic Science (UK)
Jean Cocteau once said, “If there is a defect in the soul, it cannot be corrected on the face; but if there is a defect on the face and one corrects it, it can correct a soul.”
For this reason, Dr Liz Lum YX has a special interest in acne treatment that dates back to times when she had to deal with her own acne problems and breakouts. This drove her to identify the need for innovative products and treatments to treat acne problems. She strongly believes that many acne prone patients will benefit from a combination of innovative dermatological products, lasers and medications.
Dr Liz Lum YX’s other interests include injectables such as botulinum toxins, fillers and laser treatments for pigmentary disorders. Outside of her profession, she enjoys travelling and spending quality time with her family, friends and loved ones over good meals, movies, and a cup of coffee.
Special Interest
- Acne
- Acne Scarring
- Fillers
- Neurotoxin Injection - Botulinum Toxins
- Face Lifting
- Facial Slimming and Contouring

Dr. Ian Tan
Special Interest
- Acne
- Anti-Aging
- Body Contouring
- Face Lifting
- Facial Slimming and Contouring
- Hair Regrowth
- Weight Management
Dr. Ian Tan
Dr Tan graduated from the National University of Singapore and is one of the few medical doctors selected to lead the Singapore National Healthcare Group surgical residency program. He had his basic years of training in various hospital surgical specialties and he obtained Membership of the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh (General Surgery) in 2013.
- MBBS (Singapore)
- MRCS (Edinburgh)
- GDFM (Singapore)
- GDFP Dermatology (Singapore)
- Certificate in Aesthetic Medicine, Amercian Academy of Aesthetic Medicine
- Accredited by the Aesthetic Practice Oversight Committee (Singapore Medical Council) for Certificates of Competence in Aesthetic Procedures
- Diploma in Cosmetic Science (UK)
- Accredited Family Physician
- Basic Obesity Management Accreditation 2 (BOMA 2)
- Certificate Course in Andrology
Through his practice, he developed a keen clinical interest in dermatological conditions and has obtained a Diploma in Dermatology (FP) from NUS. Dr Tan aims to help his patients achieve beauty through science by using appropriate skincare, aesthetic procedures and lasers. He believes his experience in surgery will complement his work in aesthetic and dermatological procedures at the IDS clinic.
A former national, Dr Tan was an avid athlete during his college days and developed him in local and regional canoe competitions. Outside of his profession, he enjoys running and going to the gym.
Special Interest
- Acne
- Anti-Aging
- Body Contouring
- Face Lifting
- Facial Slimming and Contouring
- Hair Regrowth
- Weight Management

Dr. Michelle Wong
Special Interest
- Acne
- Acne Scarring
- Focused Ultrasound Lifting
- Skin Brightening
- Cryo based Treatment
Dr. Michelle Wong
Dr Michelle Wong graduated from The University of Melbourne, Australia with a Bachelors of Medicine, Bachelors of Surgery and Bachelors of Medical Science. She obtained her post-graduate Diploma in Clinical Dermatology with Distinction from the Queen Mary University of London, and holds a Diploma in Aesthetic Medicine with the American Academy of Aesthetic Medicine (AAAM).
- MBBS from The University of Melbourne, Australia
- Diploma in Clinical Dermatology from Queen Mary University of London
- Diploma in Aesthetics Medicine from American Academy of Aesthetic Medicine
- Diploma in Cosmetic Science (UK)
In aesthetics, Dr Wong believes she has discovered her ikigai – the intersection of what she is both good at and loves doing. Her preferred tools of the trade are injectables such as Botulinum Toxins & fillers, which she wields with finesse and intuition - often achieving what her patients desire but cannot express through words. Out of passion and interest, she regularly attends conferences and workshops, eager to learn about the latest treatments and techniques to further hone her craft.
Combining the science of medicine with the art of beauty, Dr Wong provides an honest consult to help her patients achieve their skincare and beauty goals. She believes in understated elegance – a focus on a less-is-more approach - and works to enhance her patients’ natural features whilst instilling self-confidence. Her reassuring and gentle approach puts patients at ease allowing her to achieve maximum results through safe and effective procedures.
In her free time, Dr Wong enjoys taking long walks with her dog at the park. Her family praises her inner domestic goddess that can whip up an impressive variety of home-cooked meals. She is also active in church medical missions and believes in contributing back to society through her God-given gifts and talents.
Special Interest
- Acne
- Acne Scarring
- Focused Ultrasound Lifting
- Skin Brightening
- Cryo based Treatment

Dr. Vivian Yong
Special Interest
- Acne
- Acne Scarring
- Fillers
- Neurotoxin Injection - Botulinum Toxins
- Face Lifting
- Facial Enhancement
Dr. Vivian Yong
Dr Vivian Yong graduated from National University of Singapore in 2006, and has an experience of more than 10 years in Aesthetics. She has also accumulated extensive surgical skills and experience from various rotations in general surgery, ophthalmology, and ENT.
- MBBS
- GDFM
Dr Vivian has always had a natural inclination towards science subjects and this led her into medicine. During her medical graduate days, she developed a keen interest in Aesthetics and Skincare, and she believes that Aesthetics is one area that allows her to help a patient achieve their ideal artistic expression based on science. While Dr Vivian is always keen to accommodate her patients’ needs, she ensures that their welfare remains the utmost priority. This is why Dr Vivian is loved by her patients for always being meticulous and attentive to details.
Dr Vivian’s eye for beauty goes beyond aesthetics. Outside the clinic, Dr Vivian loves to spend her time in leather crafting and jewelry making, transforming basics into beauty. She also loves spending her quiet time exercising in the gym or chilling at home with her loved one.
Special Interest
- Acne
- Acne Scarring
- Fillers
- Neurotoxin Injection - Botulinum Toxins
- Face Lifting
- Facial Enhancement

Dr. Sean Lim
Special Interest
- Acne
- Acne Scarring
- Fillers
- Neurotoxin Injection - Botulinum Toxins
- Face Lifting
- Facial Enhancement
Dr. Sean Lim
- MBBS (Singapore)
- Certified Personal Trainer
Dr Sean is a dedicated medical professional with a diverse background in procedural disciplines and holistic care. He graduated with an MBBS degree from the National University of Singapore, earning recognition on the Dean's List for his exemplary performance in his final year Professional Examination. Fully registered with the Singapore Medical Council (SMC), Dr Sean is also certified to perform aesthetic procedures by the Aesthetic Dermatology Educational Group (ADEG).
Beyond his clinical practice, Dr Sean actively engages in community service and leadership endeavours. He has contributed his medical expertise to humanitarian missions, including Naamjai Medical Missions trips to Thailand and a collaborative effort with plastic surgeons from NUH at Yangon's Defense Services General Hospital (DSGH).
Dr Sean's commitment to excellence extends beyond the medical field. As a former Singapore national athlete in pole vaulting, he has represented Singapore in numerous international competitions, earning accolades and setting records. Dr Sean’s passion for health and fitness is evident in his certification as a personal trainer and his dedication to maintaining an active lifestyle.
A proud new father, Dr Sean cherishes quality time with his family outside of work commitments, demonstrating a balanced approach to life and well-being. His belief in delivering quality care with a personal touch reflects his ethos as a compassionate healthcare provider.
Special Interest
- Acne
- Acne Scarring
- Fillers
- Neurotoxin Injection - Botulinum Toxins
- Face Lifting
- Facial Enhancement
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
There are several causes of hyperpigmentation depending on the type. The most common cause of hyperpigmentation is prolonged exposure to the sun, which triggers the body to produce more melanin as a form of protection. This over-production of melanin causes dark spots or patches on the skin also called age spots or sun spots. After an episode of inflammation from acne, eczema, lupus or an injury to the skin, areas of the skin can also darken and this is often referred to as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Other causes include genetic predisposition, hormonal changes such as pregnancy, reactions to certain medications (anti-malarial drugs, phototoxic drugs, anti-seizure and tricyclic antidepressants), chemicals in topical treatments.
Medical conditions such as Addison’s disease and hemochromatosis can also cause hyperpigmentation in certain areas of the body, including lips, knuckles, toes and insides of the cheek.


Treatments
Treatments

Combined Treatment Plan
A combined treatment plan that includes both products and services are best for treating hyperpigmentation. Consider daily use of sunscreen and brightening skincare products that contain whitening agents like vitamin C, kojic acid, niacinamide, hydroquinone and azelaic acid, coupled with in-clinic treatments like laser therapy and chemical peels. Your medical professional should give a proper and accurate diagnosis of the dark spots before commencing treatment of hyperpigmentation.

Topicals

Orals
Prescribed medication such as tranexamic acid works by modulating blood vessels in the skin. Non-prescriptive or supplements that contain antioxidants (vitamin C and glutathione) are also recommended to help prevent the oxidative process that often leads to pigmentation in the skin.
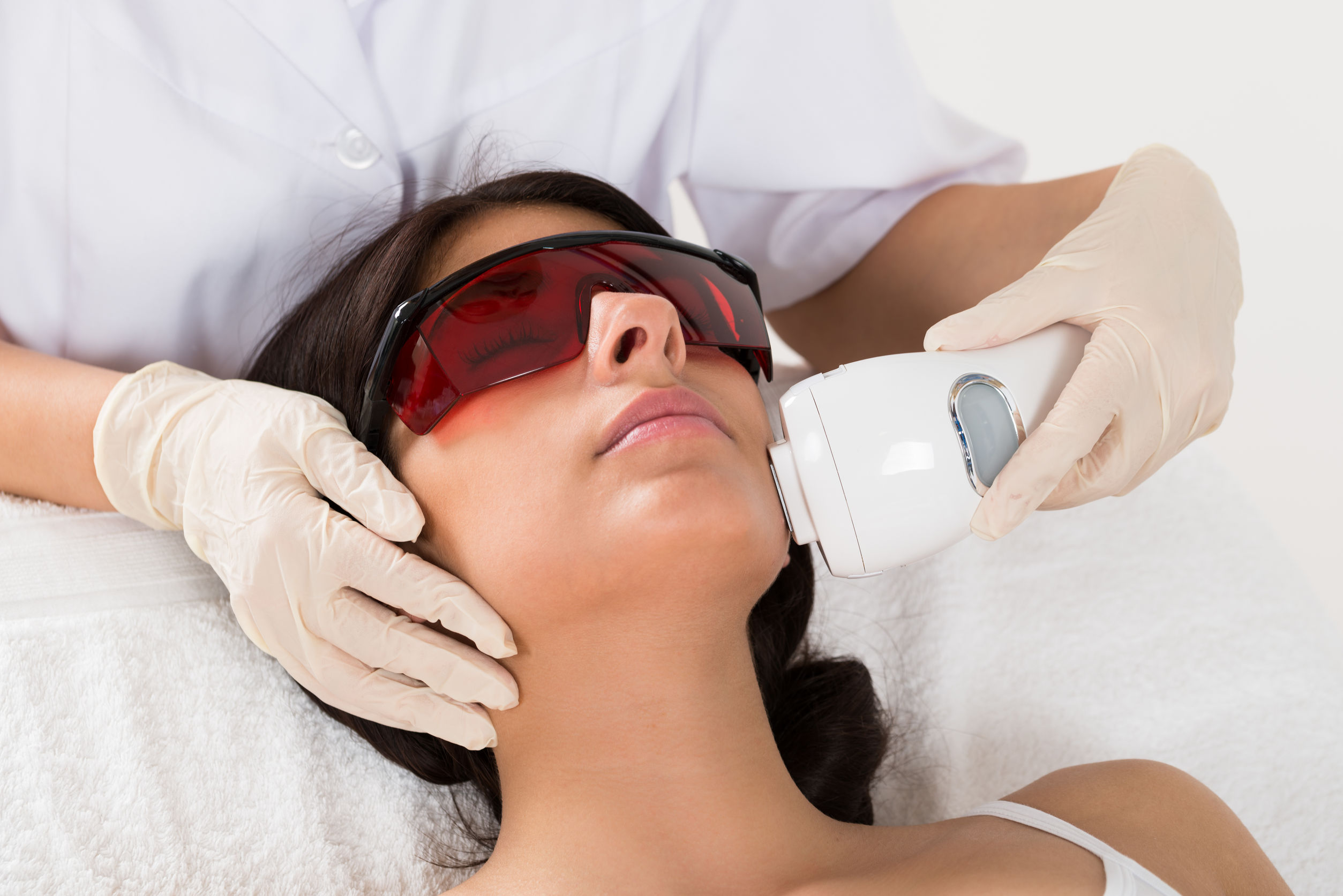
In-clinic Procedures
Medical professionals and doctors may use various procedures ranging from chemical peel, laser therapy, microneedling, to radio frequency and IPL to reduce the appearance of stretch marks. For optimum results, your medical doctor may use more than one procedure.
Types of Pigmentation
Types of Pigmentation
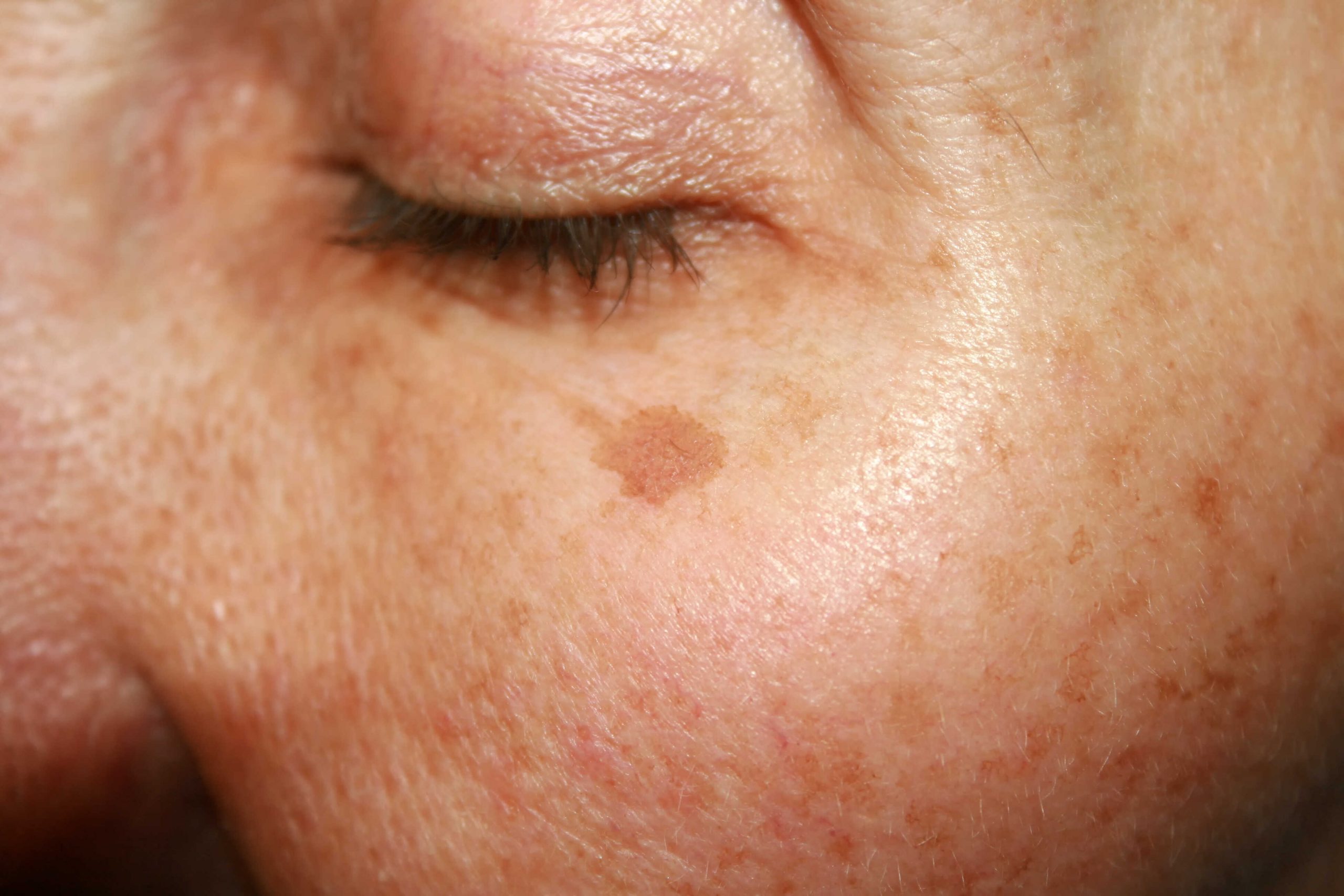
Age Spots
Commonly found on those with fair skin, age spots also known as liver spots, sun spots or solar lentigines, often appear on the face, hands and on sun-exposed areas of the body. They can vary in color from brown, gray to black, and in size, varying from very small to quite large and often appearing in groups or clusters.
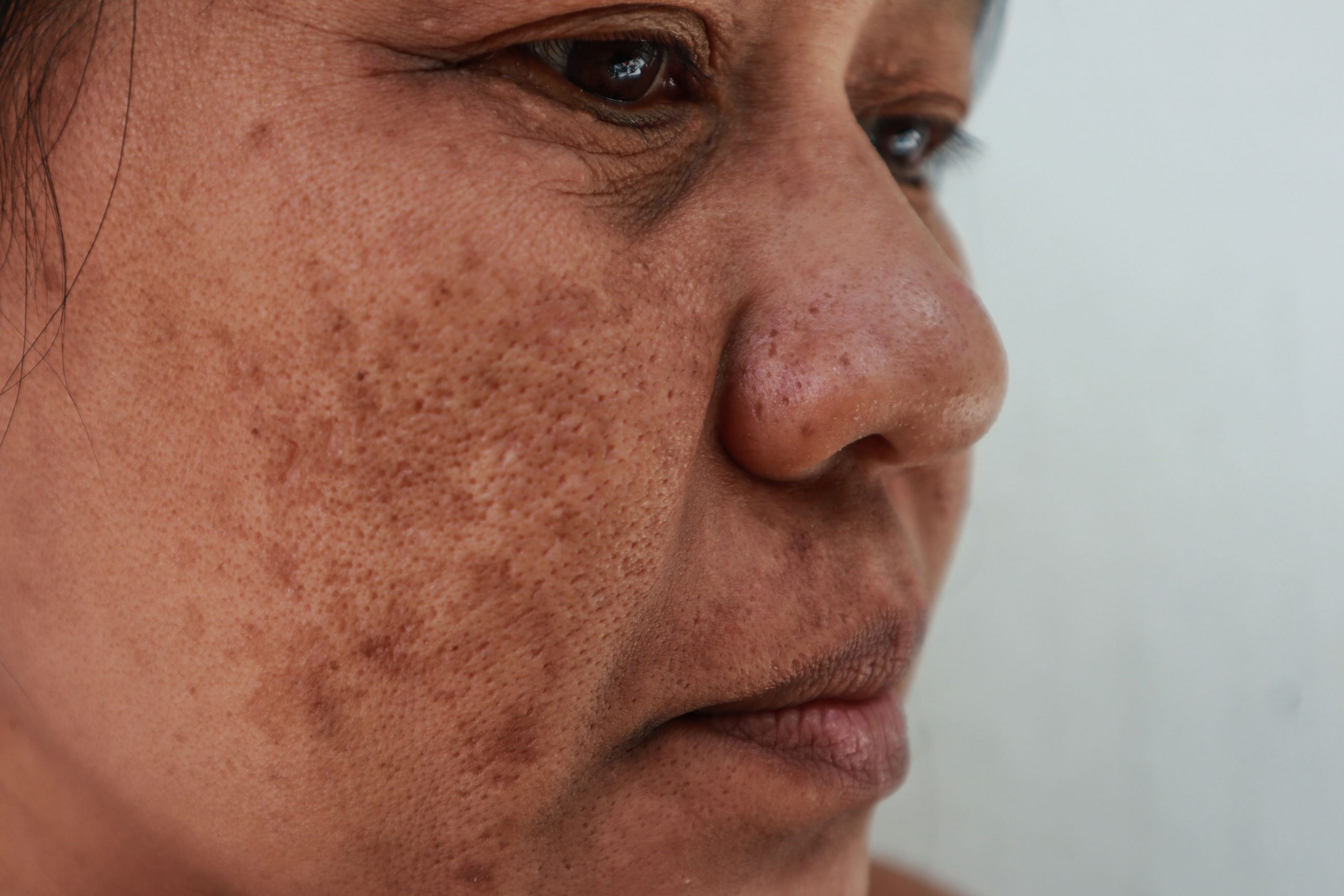
Melasma
Melasma or chloasma spots is a chronic skin condition with irregular patches of brown pigmentation commonly found on the cheeks, nose, temples and forehead during or after pregnancy or in women who are on the contraceptive pill. It is thought to be caused by increasing levels of both oestrogen and progesterone, which stimulate melanocytes resulting in increased production of the normal tanning protective chemical. It is more commonly found on Asian skin and can be extremely frustrating for those suffering from it. Melasma is more likely to occur in medium to darker skin tone as there are more active melanocytes than those with light skin. Ultraviolet light stimulates pigment-producing cells in the skin (melanocytes) to produce more melanin as a result. These brown, sun or age spots may only start to show up in your 30s as you start to age.
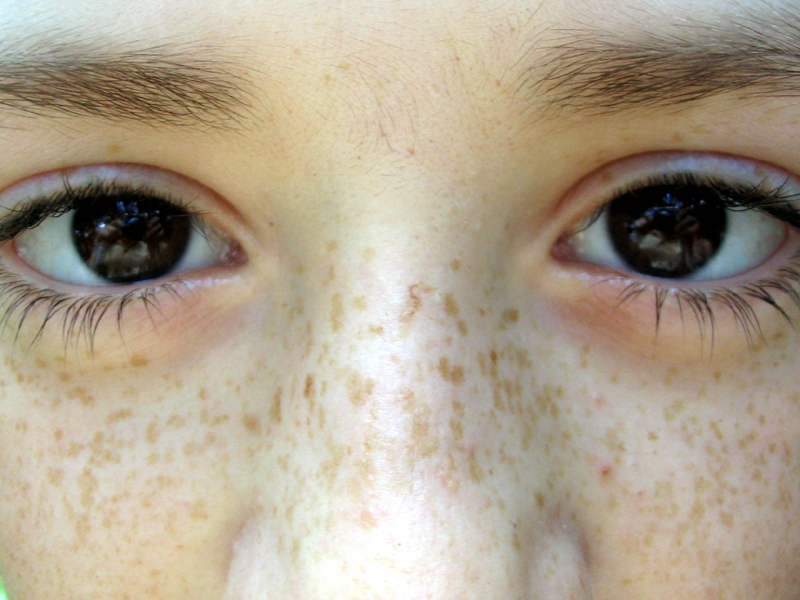
Freckles
Freckles are small brown spots that can appear on the face and body after prolonged exposure to the sun. Freckles, also known as ephelides, do not occur at birth even though they may be an inherited trait. They can occur around two to three years of age and are found more commonly on those with fair complexions. There are also certain genes that pre-dispose some to having freckles more easily. One of those genes is the MCR1 gene, also commonly referred to as the ‘red hair’ gene, which may explain the common occurrence of freckles in these individuals. Freckles may fade with age and in the winter months.
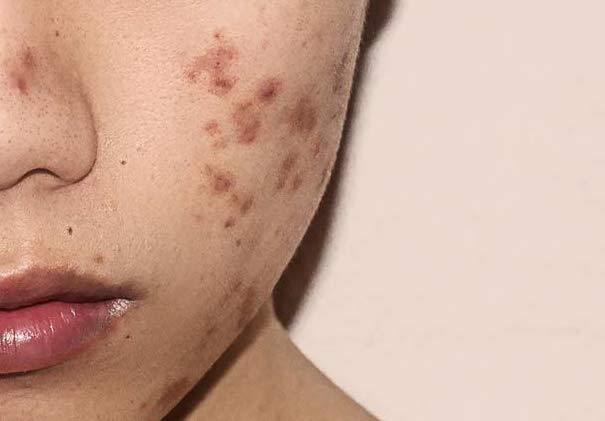
Post-Inflammatory Pigmentation (PIH)
PIH develops as a result of skin that has been damaged or undergone some form of trauma such as acne, sunburn or surgery. This is a common problem that plaques many teenagers and young adults in Singapore and the rest of Asia. These PIH spots happen more often in darker skinned individuals. The inflammatory response causes a build-up of melanin, melanin being the pigment in our pigment cells, leaving behind the brownish red blemishes on the skin which can occur anywhere on the body, face, chest and back. These marks can stay on for a few weeks to even months or years! The older we get, the slower the healing rate, and the longer the pigmentation will stay.
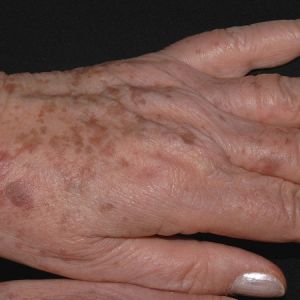
Lentigo
Lentigines are small pigmented flat or slightly raised spots with clearly defined edges. They are also a form of photo-damage caused by excessive sun exposure. But unlike freckles, lentigines usually happen much later in middle ages and they often show up in areas that are more exposed to the sun such as faces, arms, forearms, hands and legs. These pigment spots are benign and harmless. However, it may be difficult to distinguish them from malignant lesions. When in doubt, seek a medical opinion as the doctor can perform a biopsy of the lesion.
Is your pigmentation affecting your quality of life? Consult our doctors for an accurate diagnosis of your condition and a suitable treatment plan.
Book AppointmentDo's and Don't's
Do protect your skin
Maintaining and protecting good skin takes effort. Be diligent when it comes to protecting your skin from damages caused by sun exposure. Apply a broad spectrum sunscreen of SPF 30 and above daily and wear sun-protective gear and outfits.
Do see a doctor
If you have stubborn pigmentation marks that won’t go away after the use of over-the-counter remedies, do consult a medical doctor on your treatment options.
Don’t try to self-diagnose or self-medicate
While you may know of ingredients such as hydroquinone and acids that may have been proven effective in fading pigmentation spots, be sure to do a test on your skin first as they may cause a skin reaction. It is best to first check with your doctor if your dark spots are hyperpigmentation and not an indication of another medical condition.
We treat every problem in an
efficacious way.
Step into the world of aesthetic solutions built upon medical science.Where we integrate technology, artificial intelligence and complementary skincare to address the most common skin problems.
FAQs on Hyperpigmentation
Is it safe to use over-the-counter creams for hyperpigmentation?
-
While over-the-counter creams can be effective for treating mild hyperpigmentation, it is important to choose a product that is appropriate for your skin type and to follow the instructions carefully. Consult your doctor before using any new products on your skin.
How long does it take to see results from hyperpigmentation treatment?
-
The length of time it takes to see results from hyperpigmentation treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the treatment method used. Some treatments may produce noticeable results within a few weeks, while others may require several months of treatment to see significant improvement.
Can hyperpigmentation be treated on all skin types?
-
Yes, hyperpigmentation can be treated on all skin types. However, some treatment methods may be more effective for certain skin types than others.
Can hyperpigmentation be prevented?
-
Yes, hyperpigmentation can be prevented by protecting the skin from sun exposure with sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding excessive sun exposure.
Is hyperpigmentation a serious medical condition?
-
No, hyperpigmentation is not a serious medical condition and is typically considered a cosmetic concern.


